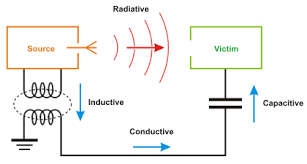
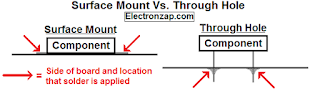
Decoupling, Bypassing and Filtering
Decoupling, Bypassing and Filtering ( 1) EMI filters can be used as a shunt element to divert electrical currents from a trace or conductor; as a series element to block a trace or conductor current; or they may be used as a combination of these functions. Selection of the filter elements should always be based on the desired frequency range and component characteristics. A low pass filter can be useful for reducing most high frequency EMI problems. It incorporates a capacitive shunt and series resistance or inductance. However, at frequency extremes, the capacitor can become inductive and the inductor can become capacitive causing the filter to act more like a band-stop filter. The filter design type should be based on the overall impedance at the circuit’s point of application for proper match. A T-filter design is effective for most EMI applications and is ideal for analog and digital I/O ports....