What is a differential pair and how does it work?
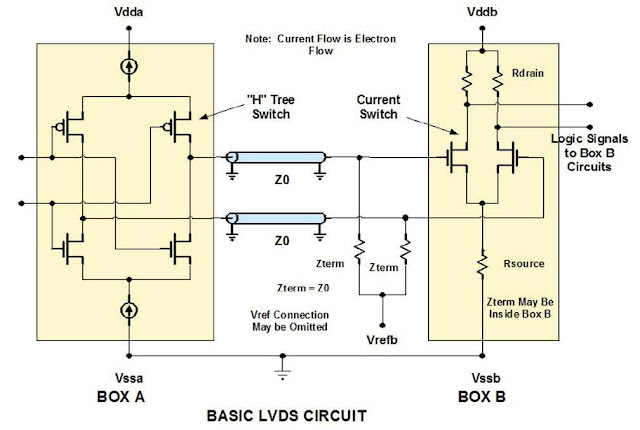
In its most basic form, a differential pair is made up of two transmission lines that have equal and opposite polarity signals travelling on them. The property that these two signals have in common is that they are equal and opposite and they are tightly timed to each other. Beyond these two characteristics there are no other properties that matter when a design uses differential pairs. Maintaining the equal and opposite amplitude and timing relationship is the guiding concept when using differential pairs. figure 1 Figure 1 is a typical CMOS differential pair driver and receiver pair. It is the usual circuit used in LVDS (low voltage differential signaling) type signaling protocols. figure 2 As can be seen from Figure 1, there are two indepe...